TEKCOOL 4000mAh Double Ended Spray Fan, Cold Air Fan, 2025 New 3 Gears USB Rechargeable Oscillating fan with LED Light Cooler Fan, Touch & Remote Control, 280ml Water Tank, Ice Filling Fan (multi)
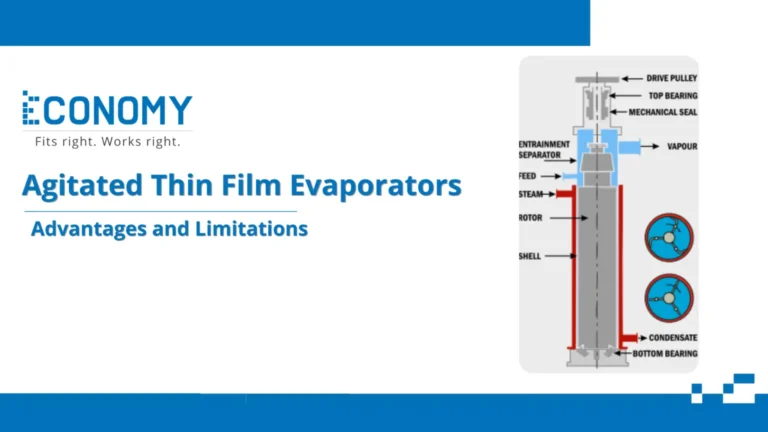
(as of March 28, 2025 21:14 GMT +05:30 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)An agitated thin film evaporator (ATFE) is a highly specialized piece of equipment designed to facilitate the efficient evaporation of volatile components from liquid mixtures. Its operation is centered around creating a thin film of liquid on a heated surface, ensuring rapid and uniform heat transfer. This is achieved using an internal rotor with blades or wipers that continuously agitate the liquid, spreading it into a thin layer as it flows down the evaporator’s cylindrical wall. The volatile components vaporize due to the applied heat, and the vapor is subsequently collected and condensed, leaving behind a concentrated product. This unique mechanism makes ATFEs particularly suitable for handling heat-sensitive or viscous materials, where conventional evaporation techniques might fall short.
Key Advantages of Agitated Thin Film Evaporators
Agitated thin film evaporators offer several advantages that make them indispensable in industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food processing. One of the most significant benefits is their ability to operate under low pressure (vacuum conditions), allowing for evaporation at reduced temperatures. This minimizes thermal degradation, making ATFEs ideal for processing heat-sensitive substances like essential oils, vitamins, and bioactive compounds.
The continuous agitation provided by the rotor ensures that the liquid film is consistently thin and well-distributed. This promotes efficient heat transfer and prevents fouling or scaling on the evaporator’s inner walls, which can be a major issue in static systems. The design also accommodates a wide range of viscosities, enabling the evaporation of thick, sticky, or sludgy materials that might clog or slow down other systems.
Additionally, ATFEs are highly adaptable, with configurations tailored to specific process requirements. Whether the goal is solvent recovery, concentration, or molecular distillation, these evaporators provide precise control over operational parameters, ensuring optimal performance. Their compact design, combined with energy-efficient operation, further enhances their appeal, particularly for applications where space and energy consumption are critical considerations.
Limitations of Agitated Thin Film Evaporators
Despite their many advantages, agitated thin film evaporators are not without limitations. One of the primary challenges is their high initial cost. The sophisticated design, coupled with the need for durable materials to withstand corrosive or high-temperature environments, makes these systems relatively expensive. For small-scale operations or those with limited budgets, this can pose a significant barrier to adoption.
Another limitation is the complexity of operation and maintenance. The rotating components and wipers require regular inspection and upkeep to ensure smooth performance. Over time, wear and tear on the rotor blades can lead to reduced efficiency or the need for replacement parts, adding to operational costs.
Additionally, while ATFEs are versatile, their performance can be limited when dealing with mixtures containing high concentrations of non-volatile solids. The accumulation of such solids can hinder the wiper’s effectiveness, leading to uneven film formation and reduced evaporation rates. In such cases, pre-treatment or alternative methods may be required, complicating the process further.
Choosing the Right Size for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate size of an agitated thin film evaporator is crucial for achieving optimal results. This decision hinges on factors such as the desired throughput, the properties of the feed material, and the specific requirements of the process. For instance, the viscosity and thermal sensitivity of the liquid being processed directly influence the surface area and rotor speed needed to create an effective thin film.
Pilot testing is often recommended to determine the best configuration for a given application. By simulating real-world conditions, operators can assess factors like evaporation rates, product quality, and energy consumption, ensuring that the chosen system meets all operational demands. Collaborating with experienced manufacturers or engineers during the design and selection process can also help address unique challenges and ensure that the evaporator is tailored to specific requirements.
Why Agitated Thin Film Evaporators Excel in Liquid Distillation
Agitated thin film evaporators are particularly powerful tools for distillation and concentration due to their ability to handle challenging materials with ease. The combination of high heat transfer efficiency, low thermal residence time, and adaptability to various operational conditions makes them ideal for separating components in complex liquid mixtures.
The thin film formation ensures rapid evaporation, reducing the likelihood of thermal damage to sensitive compounds. This is particularly beneficial in industries like pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals, where maintaining product integrity is paramount. Additionally, the vacuum operation not only lowers boiling points but also enhances separation efficiency, enabling the recovery of high-purity fractions even from mixtures with closely related boiling points.
In applications involving viscous or fouling-prone liquids, ATFEs outperform traditional methods by preventing buildup and maintaining consistent performance over extended periods. Their robust design and precise control over operational variables make them a go-to solution for processes that demand reliability, efficiency, and high-quality output.
In conclusion, How Does Work of Agitated Thin Film Evaporators are a cornerstone of modern evaporation technology. By offering unparalleled efficiency, adaptability, and precision, they address a wide range of industrial needs. While their high cost and operational complexities may pose challenges, their advantages in handling heat-sensitive, viscous, and complex mixtures make them an invaluable asset for numerous applications.






0 Comments